Aug
Blockchain in India: A New Frontier – Lead or Linger?
Introduction to Blockchain
Let us try to understand some basic terms and processes related to blockchain technology. While you read this, we believe you will understand blockchain technology better by practising it first-hand – click the link below and let us know about your experience at https://blockchaindemo.io.
Email to: piyali@piyalibagchi.com
Blockchain technology can be described as a collection of records, linked with each other which are strongly resistant to alteration because it is protected by cryptography. Here the term cryptography means an algorithm. In simple words, Blockchain runs with the help of cryptographic methods and a set of protocols that enables a network of computers to work together to securely record data within a shared open database. This database consists of a series of encrypted blocks that contain the data. (Refer to Figure 1).
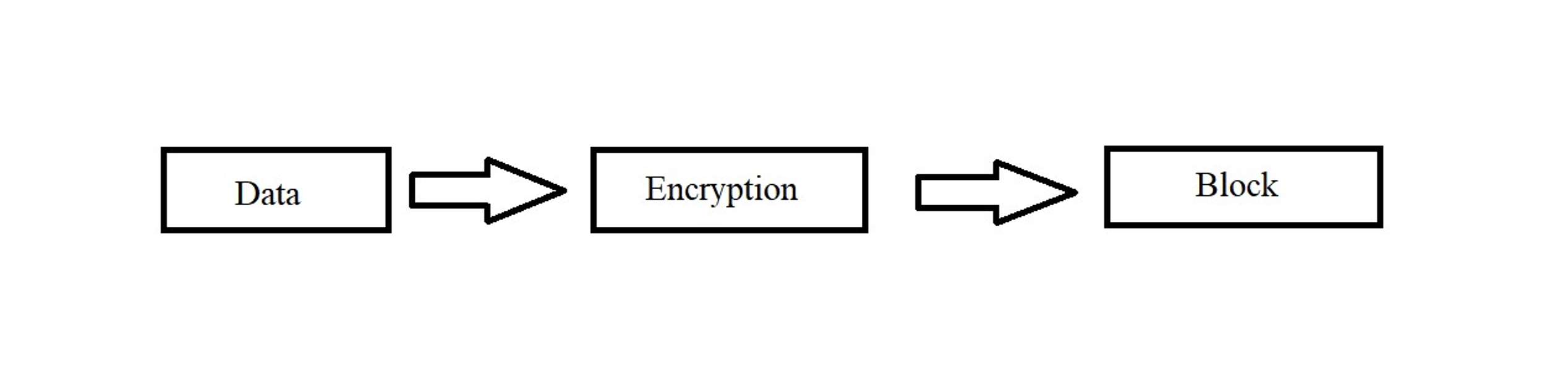
Figure 1: Formation of a Block of Data
As you see in the figure above, the blockchain is a continuously growing list of these blocks of data that are linked and secured using cryptography this makes it a trusted database with this trust being maintained by open secure computer code and encryption instead of any single institution.
The database shares and stores information in blocks that are linked together through hash values, with entries to this database being made by the computers they all will have a copy of the database and all must come to a consensus about its state before they can update it. To understand blockchain technology one must understand the notion of the blocks, mining and consensus. The Bitcoin community is the best to learn Mining from in today’s world.
What are Blocks?
If we look into the structure of the blockchain, we can see the series of blocks connected with utmost security (Refer to Figure 3). Every time participants want to add or update the information, new blocks will be added. Each block is encrypted and given a hash value which acts as a unique identifier for that particular block, but in our words, we can simply name it as a fingerprint that will be unique from others.
Before jumping into the structure of each block first, let us understand the notion of hash. Using the hashing algorithm any plain text will be converted into hashed text which consists of the “X Number” of the characters. Here we use “X number” of characters because the number of characters will be increased or decreased based upon which Secure Hash Algorithm (“SHA”) we use (Refer to Figure 2 for a better understanding of the hashing algorithm).
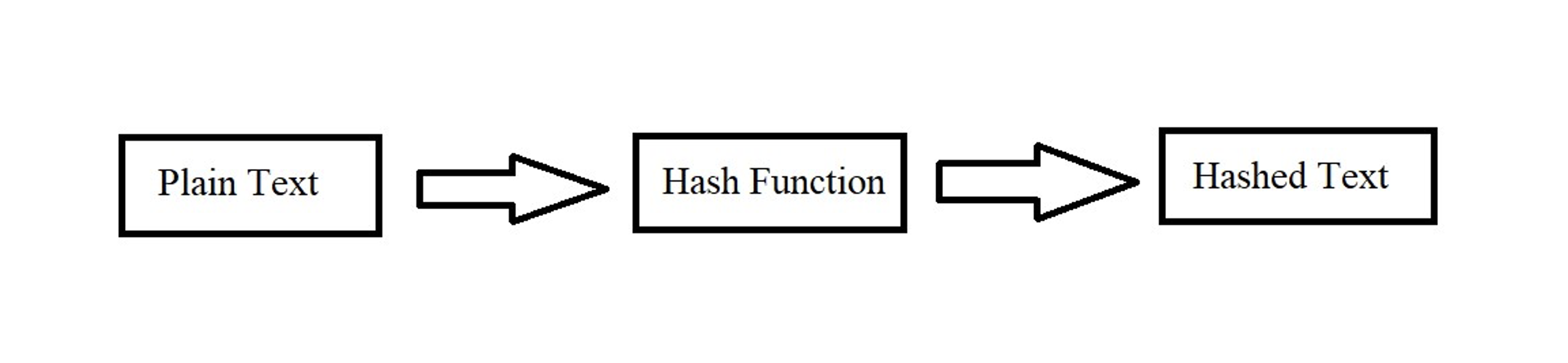
Figure 2: Hashing of Data
It is to be noted that from the plain text, we can create a hashed text but only with the help of the hashed text we cannot know what data or information has been converted into the hash. As we discussed earlier each block in the series is securely connected which means each block formed after the first block will be directly dependent on the previous hash for the creation of a new hash value for that particular block.
Further, each block contains a timestamp so that we can know every moment like what happened and when such a thing happened. With this strong connection between each block in the series of chains with the help of a unique hash, it makes it impossible for one to change or alter the data of the previous block because the next block will identify it and the entire chain will be invalid (Refer to the Figure 3). This is why many claim Blockchain to be fully secure. By clicking here, one can take a demo of how the blocks of data are created.
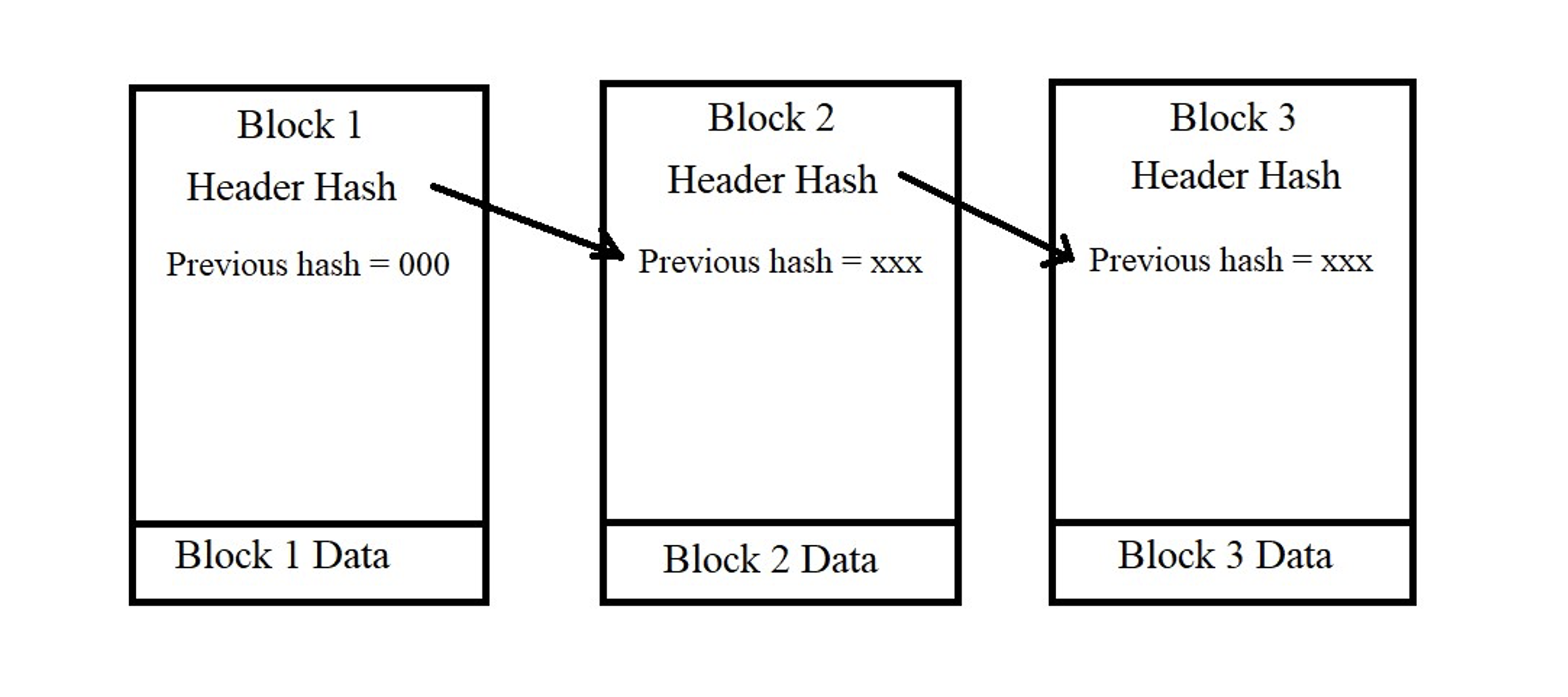
Figure 3: Formation of Chain
What is Blockchain Mining or Proof of Work?
If any new transaction or data has to be added then the miners (could be any one of us!) should solve a mathematical problem. Every miner who solves the problem first will be able to create the block but before creating it should be again accepted or verified by the other miners. Once verified this new block will be added and the miner who creates will be given incentives or rewards.
The notion of a mathematical problem is to create a new hash value for the new block. This can happen with the help of the Block number, nonce (A nonce or “number used once” is a random or semi-random number that is used only once in cryptographic communication), transaction history or data, and previous hash together if put the above-stated values in an SHA algorithm we will get the value of the hash.
Here miners will be given a target value and the hash which is calculated by the miners should be less than or equal to the given target value otherwise the block will not be a valid one. Except for the nonce, all the values and data will be the same but the nonce is a variable numerical that can be changed by the miners accordingly to reach the target value. (Refer to Figure 4).
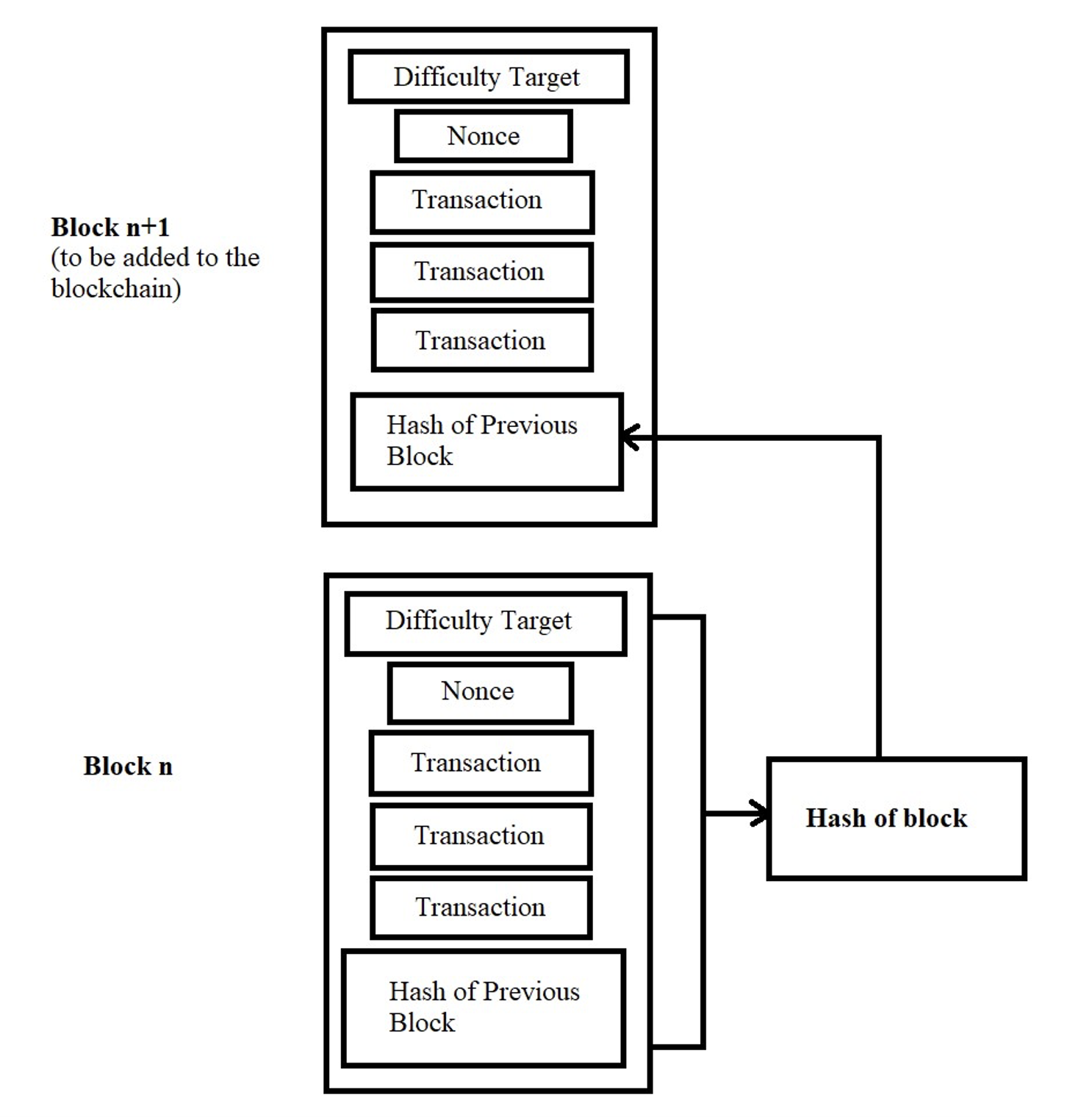
Figure 4: Visual Representation of Blockchain
What is Network Consensus?
The blockchain is a distributed ledger system which means that whatever data or information is stored in the block will be broadcast across the network. Distributed ledger technology helps to run the entire blockchain without the help of centralization. Nodes are the custodians of the blockchain. They keep all the copies of the ledger. There won’t be a single node in any network and there is no limit to the joining of the nodes in the particular network. All the nodes will have equal rights on the records stated in the ledger.
Each node will have a private key with which such node will enter the latest information or data into the ledger and the same will be broadcasted to all the other nodes and they must verify the same. The majority of the node’s opinions will be considered which is why it is the concept of network consensus. Here because of the concept of the immutable, the nodes cannot change the existing data in the ledger.
Some Advantages of Blockchain Technology:
i. Immutability: Blockchain prevents data tampering or erasing, as every entry is recorded and verified by the network members.
ii. Transparency: Blockchain allows any network member to access and verify the data recorded on the blockchain, ensuring trust and accountability.
iii. Censorship-resistance: Blockchain does not have a single point of control or authority, making it free from interference or manipulation by any party.
iv. Efficiency and speed: Blockchain streamlines and automates entries, reducing paperwork, errors, and the need for third-party verification.
v. Traceability: Blockchain creates an audit trail that documents the origin and history of an asset, enabling provenance verification and fraud prevention.
Sectors where Blockchain Technology is already implemented
Police Department:
The Firozabad police launched the "Firozabad Public Grievance Management System" to resolve public grievances efficiently. Complaints can be filed from anywhere and will automatically reach the concerned police station, with a unique token and acknowledgement sent via email or SMS. Goa police signed an MoU with blockchain startup 5ire to digitize records, becoming the first to adopt paperless documentation. This initiative aims to ensure transparency, enhance police efficiency, and make FIRs accessible to the public. Muzaffarnagar has also partnered with 5ire for a smart policing system, marking a shift towards digital governance in law enforcement1.
Revenue Department:
Telangana government has introduced the “Dharani Portal” which is built based on blockchain technology. The Portal helps everyone to access the information of the property owner and full details of the property. It also provides the functionality of changing the ownership of the property along with the complete history of the property (like a sequence of owners), the portal also validates the property of the seller2. According to the recent HMDA announcement around 1.86 documents are about to be digitalized from the year 1970 because to date the authority has already digitized documents from 19953.
Chit Funds (T-Chits Project):
The Telangana government launched T-Chits, a blockchain-based system to regulate chit-fund businesses, addressing fraud and inefficiencies. Through T-Chits, they successfully tracked ₹200 crore collected by registered chit funds and payments to 2 lakh subscribers per regulator office. With 14 offices across the state, the initiative enhances transparency and efficiency in managing chit-fund operations4.
Government - Digital Certificates and Wallet
Various state governments in India are leveraging blockchain technology to enhance the security and verifiability of digital certificates and wallets, streamlining processes and ensuring data integrity. Let us look at them:
Government of Telangana:
Due to the numerous fake student certificates Telangana government's education department started hosting the SSC certificates on the blockchain. IIIT Basara also signed an MOU with the Zebi Edu chain for maintaining all the student certificates in blockchain technology so that there won’t be the chance of producing any fake certificates or tampering with certificates5. Telangana government also decided to implement blockchain technology for certificates issued by the Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University6.
Government of Maharashtra:
Zupple start-up along with the Maharashtra government distributed blockchain “caste certificates” of more than 65,000 to the Gadchiroli tribal people with the help of “dApp LegitDoc”7. Maharashtra government also with the help of this app distributed 1 lakh diploma certificates for the students qualified from the Maharashtra State Board of Skill Development (MSBSD)8. During the pandemic, the Maharashtra government's Department of Disaster Management also implemented blockchain technology in partnership with the Print2Block startup. The department with the help of this startup-based company used to issue Covid-19 test certificates to those who got the negative result9.
Government of Tamil Nādu:
Namikkai Inaiyam blockchain backbone of Tamil Nadu launched the “e-pettagam app” which will allow the government of Tamil Nadu to secure all sorts of documents in the digital wallet. Citizens of Tamil Nadu can securely share their documents with anyone with hassle-free experience because there won’t be any tampering10.
Government of West Bengal:
Issuance of regular birth certificates leads to multiple problems individuals produce fake birth certificates to seek any benefits or the original certificates may be tampered with. That is why the West Bengal government has successfully implemented blockchain technology and started issuing digital birth certificates11.
Defence Sector
Indian Army Training Institute has signed an MOU (The Financial Express, 2022)12 with Beyond Imagination Technologies (BIT) to digitally transform the systems and processes by transitioning some aspects of it to blockchain technology. This is beneficial to allow for handling of tasks and responsibilities, reducing man-hours, increasing cost-efficiency, and prioritizing data security.
Banking and Finance Sector
The banking and finance sector is adopting blockchain to improve transaction transparency, reduce fraud, and streamline processes such as KYC (Know Your Customer) and cross-border payments.
Private Blockchain and e-rupi:
Private blockchains, unlike public blockchains, are restricted networks where access is limited to specific participants. These blockchains are controlled by a central authority or a group of organizations, ensuring more privacy, security, and faster transactions. They are commonly used in sectors like finance, supply chain, and healthcare, where data confidentiality is critical.
In the context of the Reserve Bank of India’s e-RUPI, a private blockchain could be employed to manage the distribution of vouchers, ensuring that only authorized institutions or beneficiaries can access and redeem them. This would enhance security, prevent fraud, and allow for better control over the voucher system, making it more efficient and reliable for targeted welfare distribution.
Stree Nidhi Credit Cooperatives:
StreeNidhi Credit Cooperatives is promoted by the Telangana government which provides the credit flow from the banking system to the self-help groups. Anyone can seek credit through mobile apps comfortably instead of taking loans from money lenders at high interest rates. The app usually runs with the help of blockchain technology in the areas of loan request, loan repayment, loan disbursement, loan approval and providing credit rating of each SHG member13.
Citi India:
Citi India with the ultimate aim to advance its trade digitally and to enhance the consumer's experience recently enabled letter of credit transactions with its client on blockchain technology with the help of contour. Usually, the process takes a long time but with the help of blockchain technology letters of credit can be issued in a short period14.
State Bank of India:
SBI has engaged with the US-based multinational company JP Morgan for cross-border payments with the help of blockchain technology. Blockchain technology will help customers in cost-cutting as well as making instant transactions15.
Agriculture
In agriculture, blockchain is being used to improve supply chain transparency, ensure the authenticity of produce, and facilitate efficient transactions between farmers and buyers.
Government of Telangana:
Blockchain technology has been used to a great extent in Telangana to trace the geographical locations of food products. They have traced around 360 products' origins which helped them to prevent counterfeits. Technology will generate QR codes for the seed. Mapping was done at each step the same data was stored in the disturbed ledgers for the traceability of the Tandur Tur Dal16.
Government of Jharkhand:
Jharkhand government along with the “settlemint” which is a global blockchain technology company successfully implemented blockchain technology while distributing the seeds to the farmers. The ultimate motive behind the implementation of blockchain technology is to track the seeds at multiple levels right from the hands of the agricultural department to the farmer's hands and to eliminate the middlemen availing the benefits. On implementation of blockchain technology farmers can seek a hundred per cent benefit by receiving the seeds otherwise not all farmers would be able to seek the benefits of the seed distribution scheme17.
Forensic Science Department:
Delhi government recently announced that it has adopted blockchain technology in the forensic science laboratory to ensure once the evidence is collected from the crime scene and sent to the forensic department the evidence is not tampered with. Officials said that the report at each stage will be uploaded to the block and if any person at any stage tries to tamper with the reports it cannot open because a new QR code will be generated and it alerts all other nodes immediately. Officials also stated that the “Crime and Criminal Tracking System” (CNCT) can also be used by other states18.
Health Sector:
The Rajasthan government has adopted blockchain technology in the health sector. All the electronic records of any patient such as health summary, prescriptions, requirements of any organs, and other vital reports will be mapped in the portal with utmost security. The data uploaded in the blockchain fabric ensures the genuineness of the medical records.
Government plans for Blockchain technology to be implemented across various government departments, states and sectors of India, are detailed below:
Like many plans in India go through the realm of time and patience, similarly timeline for Implementation of the blockchain technology-related plans are in the same situation, details of same are listed below:
Revenue Department, Government of Maharashtra:
Maharashtra government will be looking forward to maintaining revenue department documents digitally with the help of blockchain technology because it helps in many ways like fast documentation process, quick document verification, documents will be safe and there won’t be any sort of tampering, no chance of producing fake documents etc.
Government of NCT of Delhi:
As per the government officials soon blockchain technology will be introduced in the revenue department for digitalizing the issuance of certificates19.
Government of Karnataka:
Karnataka government is in the final stage of adopting blockchain technology to store e- registration data for the first sale unit property right from the developer's hands. According to the officials, a unique number will be generated for every registered document for deduplication. Banks will be easily able to verify the fake documents20.
Karnataka Skill Development Corporation (KSDC) is an educational institution that trains its students to build the utmost skills and knowledge and nurtures them in such a way that they will be ready to serve and help the existing and emerging industries with their skills. KSDC recently announced a tender to select a blockchain firm to issue digital certificates with the help of blockchain technology for skill-based courses21.
Pharmaceuticals:
Telangana government has implemented pilot blockchain technology in the sector of pharmaceuticals so that the supply chain will be easily noted and traceable. This reduces the chances of fake medicines entering the market22.
Banking and Finance Sector:
The Giant multinational company JP Morgan came to a consensus with India’s leading private banks which are ICIC Bank, Axis Bank, HDFC Bank, Yes Bank, IndusInd Bank and other subsidiary companies of JP Morgan to settle inter-dollar transactions with the help of blockchain technology. Usually, it takes a few hours to complete the transactions but with the help of blockchain technology, it can be completed in a fraction of a second. JP Morgan will soon launch a pilot project to observe the experiences of the banks while transactions are taking place23.
Insurance:
IRDAI Chairman Debashish Panda had given hints of the adoption of ChatGPT, Web3, and public blockchain to innovate insurance-related offerings. He focused on the improvement of the InsurTech sector in India. In his own words, "Public blockchain will further enable insurance smart contracts to contain all information in the book that would be designed to monitor live data and react accordingly, triggering an instant payout in real time”24.
Non-Governmental Organization:
SankalpTaru is an NGO with the ultimate objective of planting more and more trees across the country. SankalpTaru is one of the top NGOs in India which is why it receives donations in huge amounts from every corner of the country. SankalpTaru to build and maintain the trust among the donors recently tied up with the polygon to implement blockchain technology. Donors will get the tree data on which the amounts have been funded. Tree data will be uploaded to the blockchain so that it will have wide access where donors will get to know about the tree information instead of believing that X number of trees have been planted. Donors will get the tree URL, tree image, tree ID and geographical location25.
Agriculture:
The Kerala government decided to implement blockchain technology in the supply chain management and logistics of vegetables, milk and fish. The Kerala Development and Innovation Strategic Council will soon execute this project. The purpose of implementing blockchain technology is to track the complete chain of supply, eliminate the intermediaries seeking benefit, and maintain high quality throughout the supply chain, reducing the period. In the network of supply, each component will be given a unique ID number26.
Public Distribution System27:
The Public Distribution System (PDS) is a scheme that provides subsidized food grains and other essential commodities to the poor and vulnerable sections of society. However, it faces many challenges such as corruption, leakage, diversion, exclusion errors and lack of integration among stakeholders. Some researchers have proposed conceptual frameworks for applying blockchain technology to the PDS in India to overcome these challenges. The main idea is to use smart contracts and consortium blockchain to manage the supply chain of food grains from the warehouse to the Fair Price Shops (FPS) and the beneficiaries. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that can enforce the rules and conditions of the transactions. A consortium blockchain is a type of blockchain that is controlled by a group of authorized entities, such as the government, food corporations, FPS owners and beneficiaries.
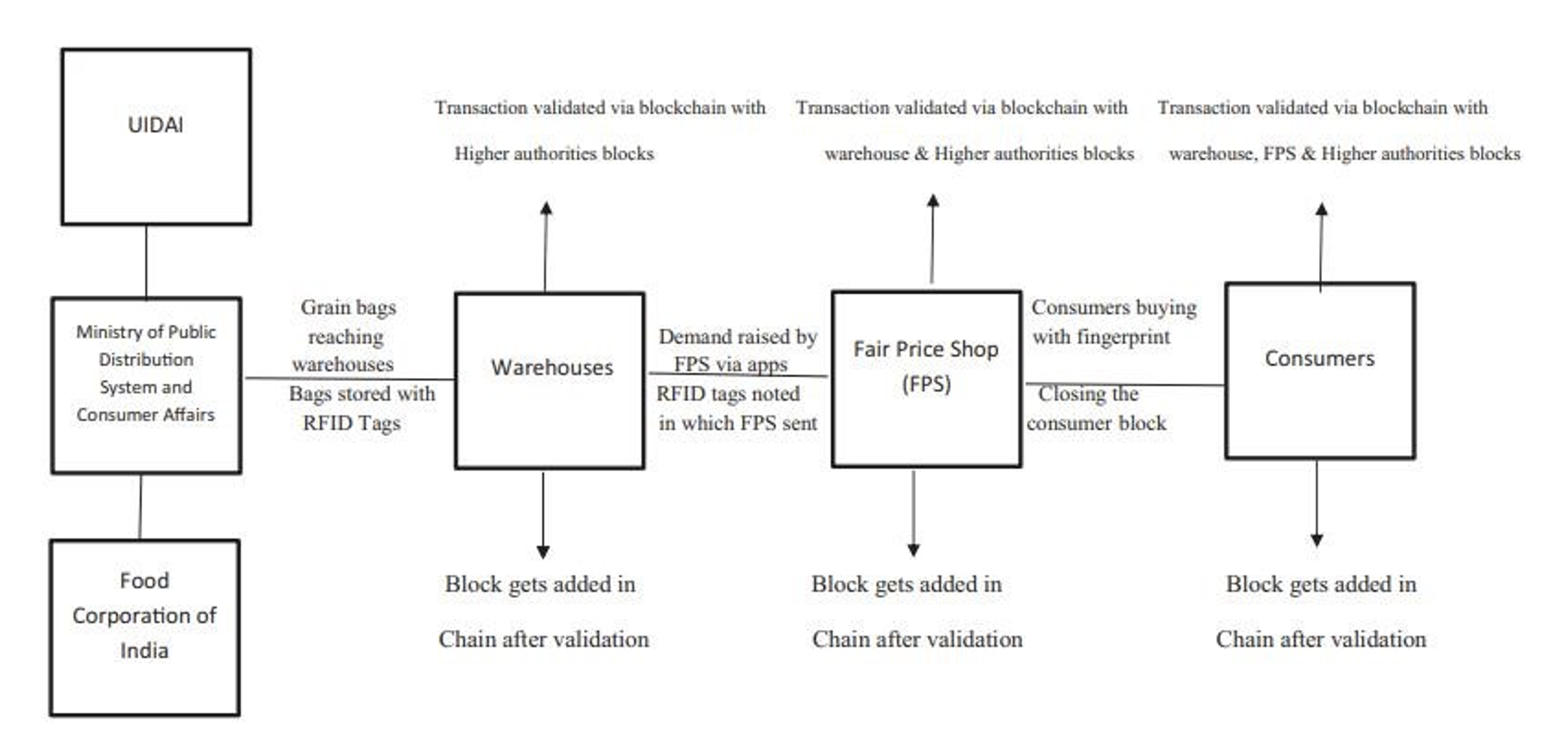
Figure 5: Blockchain-based PDS System
National Strategy on Blockchain (Government of India, 2021)28
The National Blockchain Strategy of India is a document that outlines the vision, objectives, principles, and implementation strategies for developing and deploying blockchain technology in various domains in India. It was released by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) on December 3, 2021. The main vision of the strategy is to create trusted digital platforms through shared blockchain infrastructure; promote research and development, innovation, technology, and application development; and facilitate state-of-the-art, transparent, secure, and trusted digital service delivery to citizens and businesses. However, there is no latest development on this document as of date.
GST Chain 29
The GST Chain is a blockchain-based solution proposed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC) to address challenges in India’s GST system, such as tax evasion, fake invoices, and issues with Input Tax Credit (ITC) claims. By securely recording and storing tax-related documents, the GST Chain ensures data integrity and transparency. It enables real-time monitoring of tax liabilities, instant ITC settlement, and better detection of fraud. The system seamlessly integrates with existing GST systems, enhancing trust, reducing third-party dependency, and making India’s GST framework more efficient and transparent.
Recognition of Blockchain by Indian Judiciary
The Supreme Court of India addressed the legality of cryptocurrency trading and blockchain technology in the Indian financial system. Although the case primarily focused on the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) April 2018 circular, which prohibited banks from dealing with virtual currencies, the judgment touched upon blockchain technology and its applications.
Key Views of the Supreme Court on Blockchain Technology:- Distinction Between Cryptocurrency and Blockchain: The Supreme Court made a clear distinction between cryptocurrencies (such as Bitcoin) and blockchain technology. While cryptocurrencies are a specific application of blockchain, blockchain itself is a broader technology with multiple potential uses beyond just virtual currencies. The court recognized that blockchain technology has far-reaching applications across various sectors, including banking, finance, supply chain management, and governance.
- Acknowledgment of Blockchain’s Potential: The Supreme Court also acknowledged the transformative potential of blockchain technology. It recognized that blockchain could be a key innovation in financial systems, offering secure, decentralized, and transparent systems for managing data. The court noted that blockchain’s distributed ledger technology (DLT) can significantly improve efficiency and reduce the risks of fraud, making it useful for various industries.
- No Ban on Blockchain Technology: In its ruling, the Supreme Court emphasized that the RBI’s ban targeted the trading of cryptocurrencies and not blockchain technology itself. The court observed that blockchain, as an underlying technology, has several legitimate uses beyond virtual currencies and should not be restricted. The ruling implicitly encouraged the use of blockchain in areas where it could benefit innovation and economic growth.
- Support for Technological Innovation: The judgment reflected the Supreme Court’s general support for technological innovation. The court was mindful of the importance of fostering innovation while maintaining regulatory oversight to prevent misuse. It suggested that regulatory bodies, such as the RBI, should approach technologies like blockchain with a balanced perspective that encourages innovation while addressing concerns like financial stability and consumer protection.
- Lack of Comprehensive Regulatory Framework: The court also noted that there was no comprehensive regulatory framework governing blockchain or cryptocurrency in India at the time of the judgment. While cryptocurrencies were the primary focus, the court indicated the need for appropriate regulation, which could also cover other aspects of blockchain technology. It pointed out that the absence of a clear regulatory framework led to uncertainty, which should be addressed to foster innovation.
Outcome:
The Supreme Court ultimately lifted the RBI's ban on banks dealing with virtual currency exchanges, stating that the ban was disproportionate. However, the court's views on blockchain remained positive, acknowledging its utility in various sectors without any restrictions from a legal or regulatory perspective.
Conclusion
Almost all the sectors in India would face multiple challenges at one or the other stage. Despite the regulations, and laws we could still see the lack of transparency, tampering of documents, records and shreds of evidence, authority vested in a single body, lengthy process, and inability to trace the activities but with the advent of blockchain technology we can overcome these challenges. We are aware that in today’s era, Technology plays a crucial role in human beings’ lives. From the author’s point of view, Blockchain technology can be implemented in multiple sectors for smooth and transparent functioning. In this paper, we can see the sectors that have already implemented and the sectors that are looking forward to implementing blockchain technology, in India.
In conclusion, blockchain technology represents a transformative force across various sectors, offering solutions that enhance security, transparency, and efficiency. The immutable nature of blockchain ensures that data integrity is maintained, which is crucial in applications ranging from law enforcement to financial transactions. As demonstrated by the successful implementations in regions like Telangana and Maharashtra, the potential for blockchain to streamline processes and reduce fraud is significant.
However, while the advantages are compelling, challenges such as scalability, regulatory concerns, and energy consumption must be addressed to fully harness its capabilities. Future research should focus on overcoming these obstacles and exploring innovative applications of blockchain technology. By doing so, we can pave the way for a more decentralized and trustworthy digital landscape. The journey of blockchain is just beginning, and its evolution will undoubtedly shape the future of technology and governance, provided we secure the governance related to it in due time.
1. Firozabad Police, "About FPGMS, Firozabad Public Grievance Management System," June 13, 2023, 5:15 PM, https://www.policecomplaintonblockchain.in/.
2. Telangana Government, ITE&C Department Government Of Telangana, "Hyderabad Blockchain District," June 13, 2023, 6:32 PM, https://blockchaindistrict.telangana.gov.in/ .
3. Deekshith, "HMDA to digitalize 1.86 crore documents," DECCAN Chronicle, June 13, 2023, 6:57 PM, https://www.deccanchronicle.com/nation/current-affairs/060623/hmda-to-digitalise-186-crore-documents.html .
4. Government of Telangana, "T-chits Block Chaining Chit Funds Administration," Registration & Stamps Department, June 13, 2023, 7:41 PM, https://t-chits.telangana.gov.in/ .
5. Telangana Government, ITE&C Department Government Of Telangana, "Hyderabad Blockchain District," June 13, 2023, 6:32 PM, https://blockchaindistrict.telangana.gov.in/ .
6. Aihik Sur, Blockchain tech to be used for Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad certificates, "The New Indian Express," June 13, 2023, 8:12 PM, https://www.newindianexpress.com/cities/hyderabad/2019/nov/19/blockchain-tech-to-be-used-for-jawaharlalnehru-technological-university-hyderabad-certificates-2063681.html .
7. Pratiksha BU, "Meet Blockchain Start-up Helping Maharashtra Govt. Issue Digital Certificates to Gadchiroli Tribals," The Decrypting Story, June 13, 2023, 10:11 PM, https://yourstory.com/the-decrypting-story/legitdocpolygon-blockchain-certificates-maharashtra-govt .
8. Akanksha Chaturvedi, "Maharashtra issues 1 lakh diplomas on blockchain," Business Today, June 13, 2023, 10:41 PM, https://www.businesstoday.in/crypto/story/maharashtra-issues-1-lakh-diplomas-on-blockchain343784-2022-08-05 .
9. Money Control, "Maharashtra govt onboards blockchain tech for issuing COVID-19 test certificates," Money Control, June 13, 2023, 11:22 PM, https://www.moneycontrol.com/news/business/startup/maharashtra-govtonboards-blockchain-tech-for-issuing-covid-19-test-certificates-6939661.html .
10. Rishabh Mansur, "Tamil Nadu Launches Blockchain Infra, Mobile Wallet for Securing Documents," The Decrypting Story, June 13, 2023, 11:52 PM, https://yourstory.com/the-decrypting-story/india-tamil-nadublockchain-mobile-wallet .
11. Udit Prasanna Mukherji & Suman Chakraborti, "A 1st in Bengal, baby gets block chained birth certificate," Times of India, June 14, 2023, 09:52 AM, https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/a-1st-in-bengal-babygets-blockchained-birthcertificate/articleshow/67170551.cms .
12. The Financial Express, 2022. "Beyond Imagination Technologies enters into a MoU with an Indian Army’s training institution." [Online] Available at: https://www.financialexpress.com/business/blockchain-beyond-imagination-technologies-entersinto-a-mou-with-an-indian-armys-training-institution-2714716/ [Accessed 14 06 2023].
13. Telangana Government, ITE&C Department Government Of Telangana, "Hyderabad Blockchain District," June 13, 2023, 6:32 PM, https://blockchaindistrict.telangana.gov.in/ .
14. Citigroup. "Citi India completes first Blockchain Enabled Letter of Credit Transaction on Contour," Citi, June 14, 2023, 10:12 AM, https://www.citigroup.com/global/news/press-release/2023/citi-india-completes-firstblockchain-enabled-letter-of-credit-transaction-on-contour .
15. Saikat Das & Ashwin Manikandan, "SBI joins JP Morgan's blockchain-based payment network," The Economic Times, June 14, 2023, 10:29 AM, https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/banking/finance/banking/state-bank-of-india-joins-jpmorgansblockchain-based-payment-network/articleshow/81157341.cms .
16. News & Media, "Blockchain technology helped Tandur Tue Dal bag GI Tag," Trust. Transparency. Traceability, June 14, 2023, 10:53 AM, https://trst01.com/news-media/blockchain-technology-helped-tandue-tur-dal/ .
17. NDTV, "This State Is India's 1st To Use Blockchain To Distribute Seed To Farmers," NDTV, June 14, 2023, 11:12 AM, https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/jharkhand-is-indias-1st-to-use-blockchain-technology-todistribute-seed-to-farmers-3266915 .
18. Atul Mathur, "Delhi banks on blockchain technology for tamper-proof FSL report," Times of India, June 14, 2023, 11:17 AM, https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/delhi/delhi-banks-on-blockchain-technology-fortamper-proof-fsl-report/articleshow/97359894.cms .
19. Jai Raheja, "Delhi Govt Becomes First In India To Introduce Blockchain In Forensics To Aid Crime Investigations," The 420, June 14, 2023, 11:51 AM, https://www.the420.in/delhi-govt-becomes-first-in-indiato-introduce-blockchain-in-forensics-to-aid-crime-investigations/ .
20. Nisha Nambiar, "Blockchain technology for e-registered property deals," Times of India, June 14, 2023, 12:47 PM, https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/pune/blockchain-technology-for-e-registered-propertydeals/articleshow/100434357.cms .
21. Christin Mathew Philip, "Karnataka to use blockchain tech to issue 30,000 digital certificates for skill-based courses," Money Control, June 14, 2023, 01:02 PM, https://www.moneycontrol.com/news/business/karnatakato-use-blockchain-tech-to-issue-30000-digital-certificates-for-skill-based-courses-10552081.html .
22. Telangana Government, ITE&C Department Government Of Telangana, "Hyderabad Blockchain District," June 13, 2023, 6:32 PM, https://blockchaindistrict.telangana.gov.in/ .
23. Investing.com, "JPMorgan Collaborates With Indian Banks to Incorporate Blockchain," Investing.com, June 14, 2023, 01:17 PM, https://in.investing.com/news/jpmorgan-collaborates-with-indian-banks-to-incorporateblockchain-3673023 .
24. India Today, "IRDAI chairman: Insurance sector expects innovation from ChatGPT, Web3 & public blockchain," 2023. [Online] Available at: https://www.indiatoday.in/cryptocurrency/story/irdai-chairman-focused-on-the-web3-growth-inthe-insurance-sector-to-boost-the-innovation-2339139-2023-02-24 [Accessed 15 06 2023].
25. ANI PR, "SankalpTaru Foundation becomes the First Indian NGO in Environmental Conservation Space to Launch Blockchain," The Print, June 14, 2023, 01:45 PM, https://theprint.in/ani-press-releases/sankalptarufoundation-becomes-the-first-indian-ngo-in-environmental-conservation-space-to-launchblockchain/898110/ .
26. Navanwita Bora Sachdev, Kerala Government to Use Blockchain for Supply Management, The Tech Panda, (June 14, 2023, 02:35 PM), https://thetechpanda.com/kerala-government-to-use-blockchain-for-supplymanagement/ .
27. Mishra, H., 2021. Blockchain in Indian Public Distribution System. Journal of Global Operations and Strategic Sourcing, Volume 14, pp. 10.1108/JGOSS-07-2020-0044,
28. Government of India, 2021. Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology. [Online] Available at: [Accessed 15 06 2023] https://www.meity.gov.in/writereaddata/files/NationalStrategyBCT_%20Jan2021_final.pdf .
29. National Informatics Centre. (2024). Concept Paper on GST Chain. Centre of Excellence in Blockchain Technology, Bengaluru.